
Side Effects of Dialysis in the Elderly
End-stage kidney disease requires either dialysis or a kidney transplant. While it’s a life-saving medical procedure for kidney patients, both types of dialysis procedures come with certain risks. The odds of complications are higher in the elderly.
The nephrologist in Navi Mumbai will help you weigh the risks and benefits of dialysis and offer detailed guidelines on how to manage most side effects. If you are considering dialysis but are concerned about complications, we’ve created this post that explains possible side effects and serious complications of dialysis in the elderly.
Common Side Effects of Dialysis in the Elderly
Before we dive into the side effects of dialysis, let’s understand how dialysis works.
Dialysis replicates the kidney function in people whose kidneys have stopped functioning. The procedure filters waste and fluid from the blood. Here’s what you might experience in between your dialysis sessions.
1) Fatigue and Weakness:
Dialysis can be physically exhausting, especially for elderly people with weak immune systems. Fatigue from dialysis is mainly caused by nutritional deficiency, as the process filters essential vitamins and nutrients along with waste products. Additionally, each dialysis session is pretty lengthy and may take 3-4 hours, causing fatigue.
2) Low Blood Pressure:
Too much fluid loss during dialysis can lead to a sudden drop in your blood pressure. If your blood pressure drops, you might experience additional symptoms like nausea and dizziness after dialysis.
3) Muscle Cramps:
Rapid fluid loss can cause dehydration, leading to muscle cramps. Dialysis causes electrolyte imbalance, which can result in a sudden drop in calcium, sodium, and other mineral levels. Low blood pressure can also affect blood circulation throughout the body, causing muscle cramps.
4) Itching and Dry Skin:
Skin irritation and itching are common in dialysis. Between each session, waste products build up in the blood, causing skin issues. Some people experience itching on their legs due to restless leg syndrome. Dialysis causes dehydration, which makes the skin prone to dryness and irritation.
5) Sleep Problems:
Did you know half the patients going through dialysis develop insomnia? Your kidneys filter blood regularly. However, dialysis is performed 3-4 times a week only. During this time, the waste accumulation in your body can make you feel sick. This, in turn, disrupts your sleep cycle.
Serious Complications
Dialysis can also cause long-term complications in the elderly.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Electrolyte imbalance and excess fluid buildup can cause cardiovascular disorders, such as hypertension and heart failure.
- Infection: The regular use of catheters can cause infection.
- Malnutrition: Dialysis deprives your body of vital nutrients by filtering them with waste products, which can cause malnutrition.
- Mental Health Issues: The procedure can be mentally challenging, making the patient likely to experience anxiety and depression.
Managing Side Effects
Most of these side effects are manageable with proper medication, physical therapy, and dietary modification. Contact a professional at a dialysis center in Navi Mumbai to discuss your options, the length of treatment, and frequency.
Dialysis doesn’t have to be a permanent treatment. You can opt for a kidney transplant (if you are a good candidate) to get permanent relief.

How Many Times Dialysis is Required?
Your kidneys filter blood by removing waste products and excess fluid from your body through urine. Some autoimmune diseases, diabetes, and other medical conditions can result in kidney failure. If it reaches a point where your kidneys are unable to drain excess liquid from your body, a dialysis or a kidney transplant is needed.
Dialysis performs the kidneys’ function by removing excess waste from the bloodstream. If you experience nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and swelling, visit the nearest dialysis center in Navi Mumbai and get evaluated by a nephrologist.
Factors Influencing Dialysis Frequency
Unlike kidney transplants, dialysis is not a one-time procedure. You need to schedule the treatment every week or more frequently depending on your health, the stage of kidney disease, and your doctor’s recommendation.
So, the question is, how often do you need to undergo dialysis? Let’s check out the factors that influence the frequency of this treatment.
1) Severity of the Disease:
The dialysis frequency depends on the stage of your kidney disease. If your kidney hasn’t lost its function completely, you will have fewer dialysis sessions than someone diagnosed with end-stage renal disease.
2) Type of Dialysis:
Hemodialysis is done 3-4 times weekly at a dialysis clinic. Peritoneal dialysis must be done daily.
3) Your Health:
People with diabetes, high blood pressure, and other medical illnesses that weaken their immune system might require more frequent dialysis sessions than others.
4) Doctor’s Recommendation:
Your nephrologist will assess your condition and recommend changes in the dialysis frequency based on how well your body responds to the treatment.
5) Symptoms:
If your symptoms worsen or you notice a sudden change in your health, you might have to get dialysis more frequently to manage your condition.
Standard Dialysis Schedule
Hemodialysis is the most common procedure in which blood is removed from the body and diverted to artificial kidneys, where it’s filtered and returned to the body. The procedure can last between 3 and 5 hours and is carried out 3-4 times a week, depending on your health and the severity of the disease.
You can also schedule hemodialysis five times a week and reduce the duration of each procedure to three hours. Peritoneal dialysis is done more frequently, about four times a day, and it takes up to 40 minutes per session.
Can You Change the Frequency of the Dialysis?
The frequency of kidney dialysis treatment in Navi Mumbai can be adjusted based on your health, kidney status, symptom management, and lab results (to name a few). Likewise, the frequency of the dialysis changes when you switch the type of dialysis treatment (from hemodialysis to peritoneal dialysis or vice versa).
If you are considering changing the dialysis frequency or the type, make sure you discuss it with your nephrologist first. They will offer better guidance. You must also notice your symptoms and schedule follow-up visits regularly.
Conclusion
Discuss your health and lifestyle with a nephrologist. They will guide you in choosing the best type of dialysis procedure. Home dialysis offers better flexibility. Talk to your doctor to learn more about the frequency of dialysis that will best fit your condition.

What is the Dialysis Process?
Those with failed kidneys can either get a kidney transplant or consider dialysis. The latter is an ongoing procedure, which does the work of your kidneys by filtering waste and excess liquid from your blood. The procedure is done at a dialysis center in Navi Mumbai and is considered an effective way to eliminate waste that might otherwise accumulate in your bloodstream. Patients whose 90% of the kidneys have stopped functioning are good candidates for dialysis. Let’s see the procedure, how it works, its types, and more.
Types of Dialysis
There are three main types of dialysis and each works in different ways, although the purpose of each is the same.
Hemodialysis
In hemodialysis, an artificial kidney filters your blood and returns it to your body after removing all the waste and fluid. The procedure is done 3 times a week and is usually a 3-4 hour procedure, which can be done at home or the dialysis center. Before you start dialysis, your healthcare provider will perform a small surgery to enlarge your veins so that it’s easier to insert a catheter into the veins, as well as, improve the blood flow in and out of your body.
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis filters waste from your blood through the tiny blood vessels in your abdominal lining. A special dialysis solution, containing minerals and glucose, is used to conduct kidney dialysis. The solution stays in your peritoneum overnight and the waste is collected in the dialysis solution. It can be drained into an empty bag within 60 minutes. The procedure must, however, be performed at least 4 times a day.
Benefits of Dialysis
- The procedure maintains an adequate level of calcium, potassium, and other minerals in your body.
- It’s quite effective in treating kidney failure and can do most of the job of a healthy kidney.
- Dialysis can be done at home while traveling, and when you are asleep. It’s convenient.
Risks and Complications of Dialysis
The most common risk of dialysis is the infection in the graft, which is implanted into your abdomen in peritoneal dialysis. Patients can contract peritonitis from the catheter. There’s also a risk of skin infection due to the catheter. People who choose peritoneal dialysis report excess fatigue due to the lack of protein and other nutrients. There’s also a risk of a hernia around the abdominal area.
Life After Dialysis
Life with dialysis is pretty normal. You can travel, eat, sleep, raise families, and work as usual as long as you get the dialysis treatment as and when required. You can consider self-dialysis by getting the dialysis machine and solution at home. It can also be done when you are asleep. However, dialysis is mostly seen as a temporary solution to replace your kidney function with artificial kidneys. You might eventually need to undergo a kidney transplant to ensure normal and healthy kidney function.
That was all about kidney dialysis and its types. See a kidney dialysis specialist in Navi Mumbai to learn more about the procedure and the risk factors.
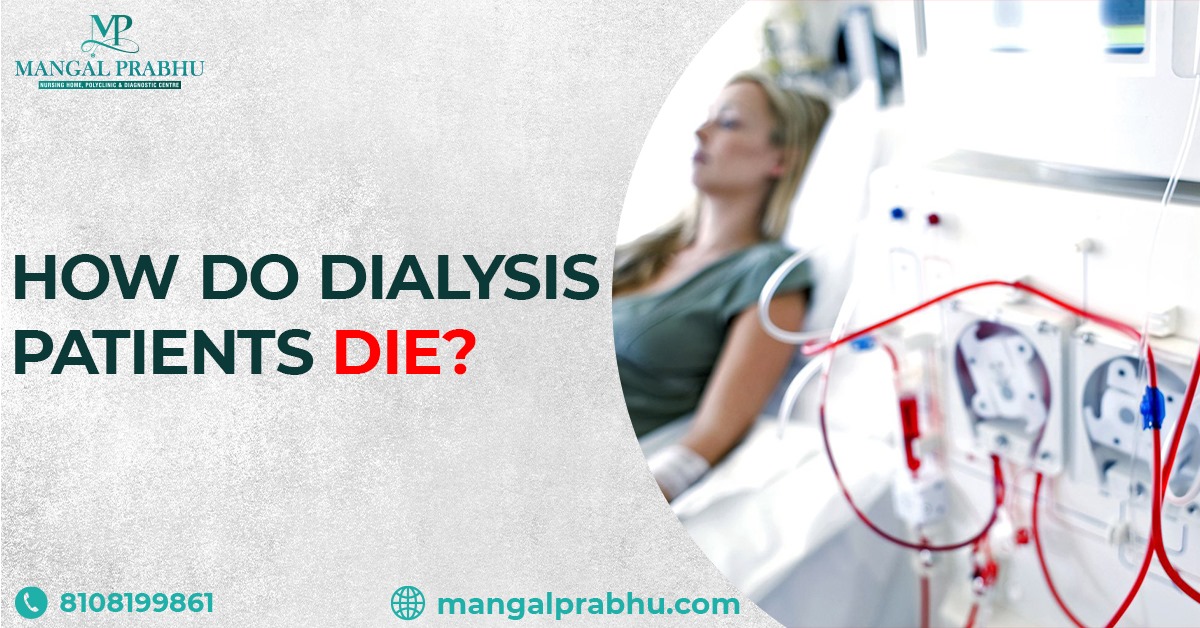
How Do Dialysis Patients Die?
Dialysis is a life-saving medical treatment for individuals with kidney failure. While it provides essential support by removing waste and excess bodily fluids, dialysis patients often face unique challenges and health risks. Here, you can explore how dialysis patients may face specific risks. Hence, understanding these risks helps you and healthcare professionals better manage and improve the care of dialysis patients.
What is Dialysis, and What Does it Do?
Dialysis is a medical procedure used to perform the critical functions of the kidneys when they can no longer do so effectively. It involves the removal of waste products and excess fluids from the blood. It helps maintain electrolyte balance and control blood pressure, ultimately prolonging kidney failure patients’ lives.
What are the Risks for Dialysis Patients?
Dialysis patients are exposed to several risks due to the chronic nature of their condition and the ongoing need for medical intervention. Some common risks include:
- Patients receiving Dialysis through a catheter or at a dialysis center are at risk of infection.
- Dialysis patients are more susceptible to heart problems.
- Chronic kidney disease often results in anemia.
- Kidney failure can disrupt the body’s balance of calcium and phosphorus.
Also Read: Preparing For Dialysis: What To Expect?
What Causes Dialysis Patients to Die?
Several factors contribute to the mortality of dialysis patients:
Cardiovascular Disease: Cardiovascular issues are a leading cause of death in dialysis patients. The strain on the heart and blood vessels due to fluid and electrolyte imbalances can result in heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure.
- Dialysis patients have weakened immune systems and are at higher risk of infections, which can become severe and life-threatening.
- Infections, if left untreated, can progress to sepsis, a severe response of the body to infection that can lead to organ failure and death.
- Complications related to dialysis access, such as infections or clotting, can lead to serious health issues.
- Dialysis patients may struggle with malnutrition due to dietary restrictions and loss of appetite, making them more susceptible to infections and other health problems.
How Can Dialysis Patients Reduce Their Risks?
At Mangal Prabhu Hospital, you can find a team of experienced Nephrologist in Navi Mumbai who provide specialized care for kidney-related conditions. Moreover, dialysis patients can take several steps to reduce their risks and improve their overall quality of life:
- Consistency in attending dialysis sessions and following prescribed treatment plans is crucial.
- Taking medications as prescribed to control blood pressure, anemia, and other complications is vital.
- Working with a registered dietitian to develop a kidney-friendly diet can help manage complications and maintain overall health.
- Proper hygiene, catheter care, and regular vaccinations can help prevent infections.
- Frequent visits to a nephrologist or healthcare provider are essential for monitoring overall health and addressing emerging issues promptly.
Conclusion
While Dialysis is a life-sustaining treatment for individuals with kidney failure, it has risks. Understanding these risks and their causes is essential for patients and healthcare professionals. At Mangal Prabhu Hospital, a trusted Dialysis Center in Navi Mumbai, experienced nephrologists work closely with patients to provide comprehensive care to improve the quality of life for dialysis patients. By adhering to treatment plans and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, dialysis patients can reduce their risks and maximize their chances of leading fulfilling lives despite their medical condition.

End-stage Renal Disease
End-stage renal disease, or kidney failure, occurs when your kidneys fail to function and can no longer filter the blood normally. As a result, you might need a kidney transplant or dialysis from a kidney specialist in Navi Mumbai. Your kidneys are responsible for excreting the waste and fluid from your blood through urine. When they stop functioning, these waste particles and excess fluid build up in your blood.
The fifth stage of kidney disease is life-threatening and can result in loss of life if not addressed immediately. In addition to filtering blood, your kidneys are responsible for striking a perfect balance between salt, minerals, and water in your body. They create urine so that excess waste can be excreted.
Causes of End-Stage Renal Disease
Kidney disease can occur due to a number of health conditions, a sedentary lifestyle, and a poor diet. It can damage your kidneys at once or cause slow damage, which eventually develops into chronic kidney disease.
Here are the common causes of end-stage renal disease:
- Birth defects
- A history of severe urinary tract infections that occurred repeatedly
- Heart disease or hypertension
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Lupus and other autoimmune diseases
- Kidney stones
- Diabetes
Sometimes, chronic kidney diseases, like cancer, can cause kidney failure. Whatever the cause is, it’s important to see a urologist in Navi Mumbai immediately if you notice any or all of the below symptoms.
Symptoms of End-Stage Renal Disease
Unfortunately, kidney diseases don’t produce any serious symptoms initially. As the condition progresses and your kidney fails, you might notice the below symptoms.
- Excess fatigue and weakness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swollen ankles and feet
- Muscle cramps
- Itching
- Loss of appetite
- Unusual changes in urination
- High blood pressure
- Difficulty in concentration
- Chest pain and shortness of breath due to fluid buildup
Contact a urologist immediately if you notice these symptoms. These are often the signs that your kidney has stopped functioning, and you might need immediate treatment. However, these symptoms can also indicate other health problems, which aren’t as serious as end-stage renal disease. It’s best to consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive diagnosis.
Treatment for End-Stage Renal Disease
A kidney transplant is a permanent solution to end-stage renal disease. In transplant surgery, the surgeon will replace the damaged kidney with the kidney of a living person or a deceased.
Everyone has two kidneys, and it’s totally possible to live with one. Before the transplant, the surgeon will conduct a few tests to ensure the donor’s kidney is a good match for you. After the transplant, you may have to take immune-suppressant medications to prevent your immune system from rejecting the new kidney, assuming it is a foreign object. Once the transplant is done successfully, your new kidney will start functioning like normal.
If you are considering dialysis, know that you will have to take dialysis treatment till the transplant surgery. Visit a dialysis center in Navi Mumbai to discuss the dialysis procedure, how frequently you need that, and which dialysis is best for your condition.
What Is the Difference Between Hemodialysis and Dialysis?
The kidneys are one of the major organs in the human body and perform multiple functions. They help remove waste products generated in the body through diet metabolism. The waste is excreted out of the body in the form of urine. The kidneys also remove excess salt, water, many drugs which we consume, regulate acid and potassium content in the body and help balance the body fluids. Kidneys also secrete hormones that trigger production of red blood cells in the body, regulate blood pressure. Kidneys also produce an active form of Vitamin D that is required for strong and healthy bones, a kidney specialist in Navi Mumbai.
Needless to say, kidneys are prone to various ailments and conditions including kidney failure. Kidney failure may be Reversible- meaning, it can be recovered with treatment. End-stage or chronic kidney failure is one in which kidneys are no longer able to cope and dialysis and transplant are the only options.
Dialysis is a treatment in which the blood of patients with kidney failure is cleaned through artificial means, either outside the body or inside the body. Combined with other medication, dialysis helps the patient of end-stage kidney failure live longer which is carried out at a dialysis center in Navi Mumbai.
Types Of Dialysis:
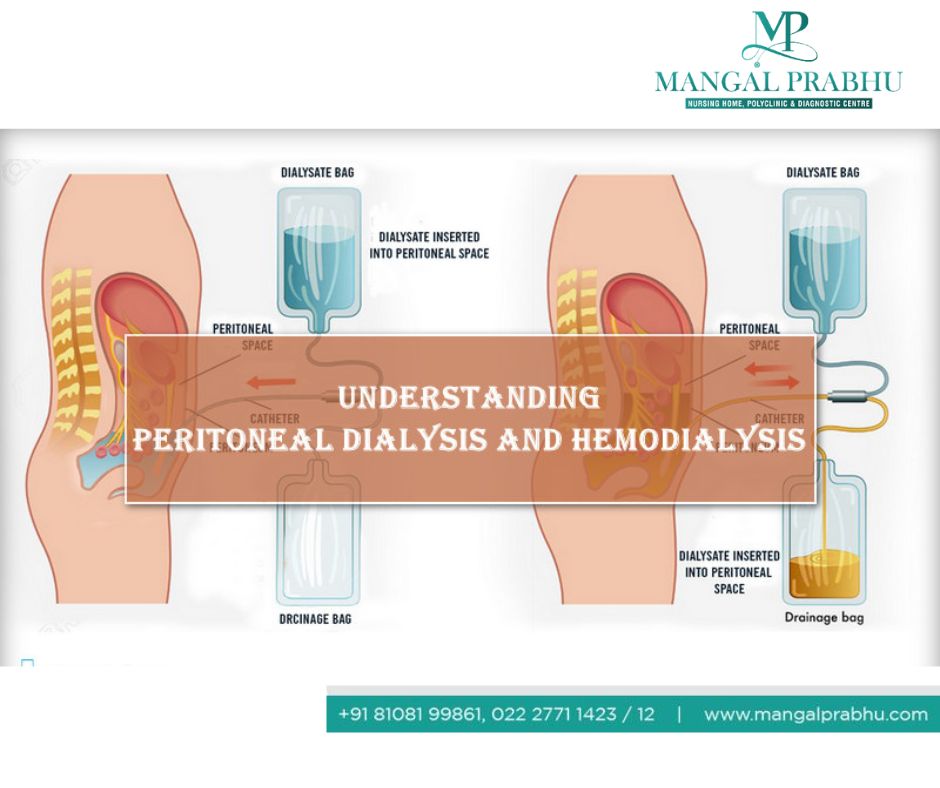
There are 2 types of dialysis: Hemo and Peritoneal.
In Hemodialysis, the blood is cleaned outside the body using a dialysis machine and then sent back into the body. This can be done either at a hospital or at home. In peritoneal dialysis, a special liquid is put in the abdomen. As blood passes through blood vessels in the abdominal cavity, this liquid absorbs waste from them across the peritoneal membrane (lining of our abdomen). This polluted liquid is then drained away.
Difference Between The Two Types:
Hemodialysis
- Where it is done: At home or a hospital.
- How often it is done: 3 to 5 times a week.
- Complexity of the procedure:
The dialysis machine (dialyzer) requires a vascular access which is basically a pair of artery and vein through which the blood in the body is pulled out of the body and in to the machine, cleaned using special filters and then cycled back to the body. Initially access is achieved by placing a temporary catheter in central veins, usually in the neck. Later a surgery is done to create a fistula in the forearm.
- Ability to work: During the entire duration of the dialysis, the patient is either sitting or lying on bed and cannot perform any other activities. Rest of the days, they are free to work.
- Side effects of the procedure: Fatigue, low blood pressure.
- Diet Restrictions: Salt and water intake are mainly restricted along with certain other food items which have high potassium and phosphorous.
Peritoneal Dialysis
- Where it is done: At home
- How often it is done: Daily, 4 to 6 times per day or in the night.
- Duration of the procedure: 3 to 5 hours per day in total
- Complexity of the procedure:
Using laparoscopic surgery, a peritoneal catheter is inserted into the lining of the abdominal wall (peritoneum), which provides an access to the abdominal cavity. The patient can use this access 2 weeks after it has been created.
On a daily basis, the patient must fill the abdominal cavity with a special fluid (dialysate filter), through this access point. The fluid cleans the blood through the internal walls of the abdomen and then drains into a collection bag which the patient or a caretaker must empty out.
- Ability to work: This procedure can be done at night, which means, the patient can perform his/her normal activities during the day. The person can even travel, as long as he/she is able to perform this procedure on his/her own, in a clean place.
- Side effects of the procedure: Risk of infection of the Catheter(or) abdomen and limitation of membrane function.
- Restrictions: There are fewer restrictions to diet with this procedure compared to hemodialysis.
What is the importance of dialysis? Which patients require it the most?
Dialysis
Dialysis is an artificial way of carrying out the functions of kidneys. People who have failed or damaged kidneys may have difficulty eliminating waste and unwanted water from the blood. With the help of dialysis treatment in Navi Mumbai these process can be done artificially. It is also known as Renal Replacement Therapy(RRT).
The kidney’s function is to regulate the body’s level of water and minerals and remove waste. But dialysis has some limitations such as the kidney can also secrete certain products that are important in metabolism whereas dialysis is not able to do this.
Who needs Dialysis?
A person whose kidneys only works 10-15% of their capability is someone who is in need of dialysis. According to a survey around 14% of adults aged above 30 have chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Kidneys filter around 120 to 150 quarts of blood each day-if they are healthy. If the kidneys are not filtering the blood properly the waste builds up in the blood that might cause coma and even death. With the help of dialysis, we can prevent the waste products in blood from reaching hazardous levels.
Types of Dialysis
There are variety of dialysis. But most common dialysis are majorly three.
- Intermittent haemodialysis
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Continuous renal replacement therapies (CRRT)
Let’s discuss each of them briefly to understand them.
INTERMITTENT HEMODIALYSIS
In this dialysis the blood circulates outside the body. It goes through a machine with special filters. In this we use a flexible tube known as catheter which is inserted into the vein through which the blood comes out. Just like the kidneys the filters also cleanse the blood removing the waste product from the blood. The filtered blood then returns to the patient through another catheter. This works like an artificial kidney.
To insert catheters surgery is done to enlarge a blood vessel usually in the arm making it possible for the catheter to enter easily.
This filtration or haemodialysis is usually done three times a week, for 3 to 4 hours a day, depending on the wellness of kidney.
Haemodialysis can be done at a special dialysis center or at home.
But if you are willing to have haemodialysis at home you must have caretaker who knows exactly what to do in dialysis and home must also be suitable for taking haemodialysis equipment.
- PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
Peritoneal dialysis is based on the principle of diffusion.
In this dialysis process a sterile dialysate solution rich in minerals and glucose us run through a tube into the peritoneal cavity, the abdominal body cavity that surrounds the intestine. It has a semi-permeable membrane, the peritoneal membrane.
Peritoneal dialysis is less efficient than haemodialysis. It takes longer periods, and it removes around the same amount of total waste product as haemodialysis.
As it can be done at home it is more convenient and comfortable giving patient more freedom and independence. It can also be done while travelling as it requires minimum of specialized equipment.
There are two main types of peritoneal dialysis
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
It requires no machinery and even the patient can do it. This happens every day, four or five times per day
- Continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis (CCPD)
It uses a machine to exchange fluids. It is generally done every night, while the patient sleeps. It usually takes around 10-12 hours.
This is more convenient to elderly people, infants and children.
- CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT DIALYSIS
This dialysis can be intermittent or continuous.
While a session of intermittent dialysis lasts for up to 6 hours, continuous renal replacement are designed for 24 hour use in an intensive care unit(ICU).
It can involve either interaction or diffusion. It is better tolerated than intermittent dialysis, because the process is slower. This leads to fewer complications.
With all these types of dialysis there are a few risks that comes along. A few of them are
- Hypotension
- Cramps
- Nausea
- Headache
- Back pain
- Chest pain
- Fever
- Chills
Symptoms of kidney failure
We humans can work on a single kidney even after we all have two kidneys. Symptoms may vary from people to people. Some of them may include:
- Fatigue
- Increasingly frequent need to urinate
- Erectile dysfunction
- Nausea
- Blood in urine
- Blood in semen
- Protein in blood
Doctor After diagnosing kidney failure we go for dialysis. But it also comes with a few side effects which are
- Muscle cramps
- Low blood pressure
- Sleep problems
- Depression
- Fluid overload
Kidney is an important part of human body, so any disease relating to kidney is very serious condition and should be taken very seriously. Once the kidneys fail, they are unlikely to recover but with the help of dialysis we can enhance our wellbeing and prolong life for up to 20 years or more.
- STAY HEALTHY, STAY SAFE!
