The kidneys are one of the major organs in the human body and perform multiple functions. They help remove waste products generated in the body through diet metabolism. The waste is excreted out of the body in the form of urine. The kidneys also remove excess salt, water, many drugs which we consume, regulate acid and potassium content in the body and help balance the body fluids. Kidneys also secrete hormones that trigger production of red blood cells in the body, regulate blood pressure. Kidneys also produce an active form of Vitamin D that is required for strong and healthy bones, a kidney specialist in Navi Mumbai.
Needless to say, kidneys are prone to various ailments and conditions including kidney failure. Kidney failure may be Reversible- meaning, it can be recovered with treatment. End-stage or chronic kidney failure is one in which kidneys are no longer able to cope and dialysis and transplant are the only options.
Dialysis is a treatment in which the blood of patients with kidney failure is cleaned through artificial means, either outside the body or inside the body. Combined with other medication, dialysis helps the patient of end-stage kidney failure live longer which is carried out at a dialysis center in Navi Mumbai.
Types Of Dialysis:
There are 2 types of dialysis: Hemo and Peritoneal.
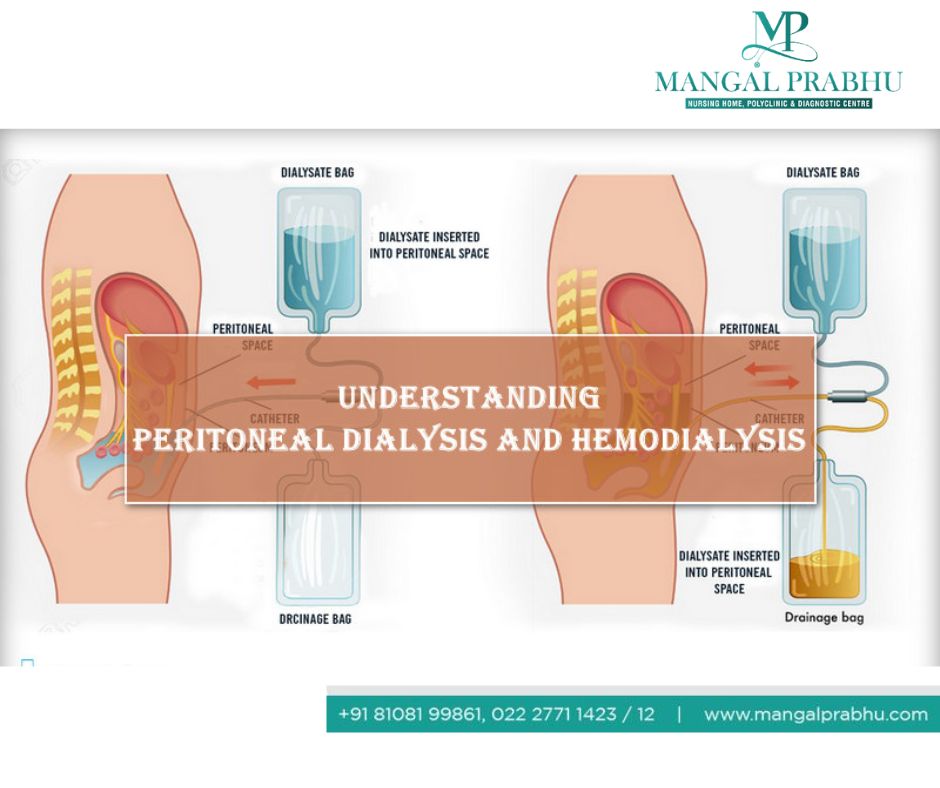
In Hemodialysis, the blood is cleaned outside the body using a dialysis machine and then sent back into the body. This can be done either at a hospital or at home. In peritoneal dialysis, a special liquid is put in the abdomen. As blood passes through blood vessels in the abdominal cavity, this liquid absorbs waste from them across the peritoneal membrane (lining of our abdomen). This polluted liquid is then drained away.
Difference Between The Two Types:
Hemodialysis
- Where it is done: At home or a hospital.
- How often it is done: 3 to 5 times a week.
- Complexity of the procedure:
The dialysis machine (dialyzer) requires a vascular access which is basically a pair of artery and vein through which the blood in the body is pulled out of the body and in to the machine, cleaned using special filters and then cycled back to the body. Initially access is achieved by placing a temporary catheter in central veins, usually in the neck. Later a surgery is done to create a fistula in the forearm.
- Ability to work: During the entire duration of the dialysis, the patient is either sitting or lying on bed and cannot perform any other activities. Rest of the days, they are free to work.
- Side effects of the procedure: Fatigue, low blood pressure.
- Diet Restrictions: Salt and water intake are mainly restricted along with certain other food items which have high potassium and phosphorous.
Peritoneal Dialysis
- Where it is done: At home
- How often it is done: Daily, 4 to 6 times per day or in the night.
- Duration of the procedure: 3 to 5 hours per day in total
- Complexity of the procedure:
Using laparoscopic surgery, a peritoneal catheter is inserted into the lining of the abdominal wall (peritoneum), which provides an access to the abdominal cavity. The patient can use this access 2 weeks after it has been created.
On a daily basis, the patient must fill the abdominal cavity with a special fluid (dialysate filter), through this access point. The fluid cleans the blood through the internal walls of the abdomen and then drains into a collection bag which the patient or a caretaker must empty out.
- Ability to work: This procedure can be done at night, which means, the patient can perform his/her normal activities during the day. The person can even travel, as long as he/she is able to perform this procedure on his/her own, in a clean place.
- Side effects of the procedure: Risk of infection of the Catheter(or) abdomen and limitation of membrane function.
- Restrictions: There are fewer restrictions to diet with this procedure compared to hemodialysis.



