A Comprehensive Guide to Gallbladder Stone Removal
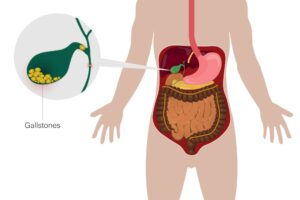
The organ known as the gallbladder, which is located underneath the liver, generates suspended solids called gallstones. They are made up of calcium salts, bile pigments, and cholesterol. Gallstones can be single or multiple and vary in size from tiny stones to big golf balls.
Whenever gallstones obstruct the bile ducts, which are tubes that convey bile from the liver to the small intestine, difficulties might result. Pain, inflammation, infection, and other problems may come from this. Gallstones can cause symptoms varying from none at all for some people to severe upper right abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and fever for others.
According to a Surgery Hospital in Navi Mumbai, a medical operation called gallbladder stone removal removes gallstones from the gallbladder. Abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, and bloating are just a few of the symptoms that gallstones can produce. They can also result in consequences like inflammation, infection, and jaundice. The removal of gallbladder stones can be accomplished through surgery, non-surgical approaches, and a variety of medications.
Medication:
Medication might be the best course of action for those with little gallstones that are not generating noticeable symptoms. Gallstones can be eliminated throughout the period with the use of drugs like Ursodiol and Chenodiol. These drugs function by lessening the amount of cholesterol the liver produces, which can aid in preventing the development of new gallstones and dissolving old ones.
Also Read: Do I Need Surgery For Hernia?
Nonsurgical Techniques (Gallbladder Stone Removal Without Surgery):
The removal of gallstones can be accomplished by a number of non-surgical techniques. These treatments are frequently done as outpatients and don’t call for a night in the hospital. They consist of:
- An endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera, and a light at the end are used during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to view the bile ducts. The gallstones are extracted using a tiny basket once the bile ducts have been discovered and a little incision has been created in the duct.
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL): During this operation, gallstones are broken up into smaller pieces using shock waves so that they can be expelled from the body through the bile ducts.
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC): During this operation, a needle goes under the skin into the liver and into the bile ducts to inject a dye. The gallstones then are located using X-rays, and a tiny incision is performed.
Surgery (Gallbladder Stone Removal Surgery):
Surgery may be required to extract the gallbladder in patients with bigger or more numerous gallstones. As per a General Surgeon in Navi Mumbai, laparoscopic surgery is the most common surgery for removing the gallbladder. It involves several small abdominal incisions and the use of a laparoscope, a thin, illuminated tool, to remove the gallbladder.
Compared to conventional surgery, this method requires less recuperation time and is less intrusive. The gallbladder may sometimes require to be extracted by surgical intervention. This surgery entails making a bigger abdominal incision and removing the gallbladder by hand. Patients who are poor candidates for laparoscopic surgery often undergo open surgery.
Recovery (Gallbladder Stone Removal Recovery Time):
According to the procedure used, the recovery period after gallbladder stone removal varies. Recovery from medication and non-surgical methods is frequently quicker than from surgery. Surgery patients might feel some discomfort and pain for a few days following the procedure, and they might need to limit their physical activity for a few weeks.
Patients will need to adjust their lifestyles following gallbladder ectopy in order to make up for the absence of the organ. Patients may feel alterations in digestion because the gallbladder controls the storage and release of bile, especially after consuming fatty or oily foods. To encourage healthy digestion and avoid difficulties, it is crucial for individuals to maintain a healthy diet and engage in regular exercise.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the removal of gallstones from the gallbladder is a routine medical treatment. Medication, non-surgical treatments, and surgery are just a few of the ways that gallbladder stones can be removed. The size, location, and general health of the patient all factor into the recommended course of treatment. Healing times vary according to the procedure type, and patients may need to adjust their lifestyles to account for the removal of their gallbladder.
