Causes of Left-sided Pleural Effusion
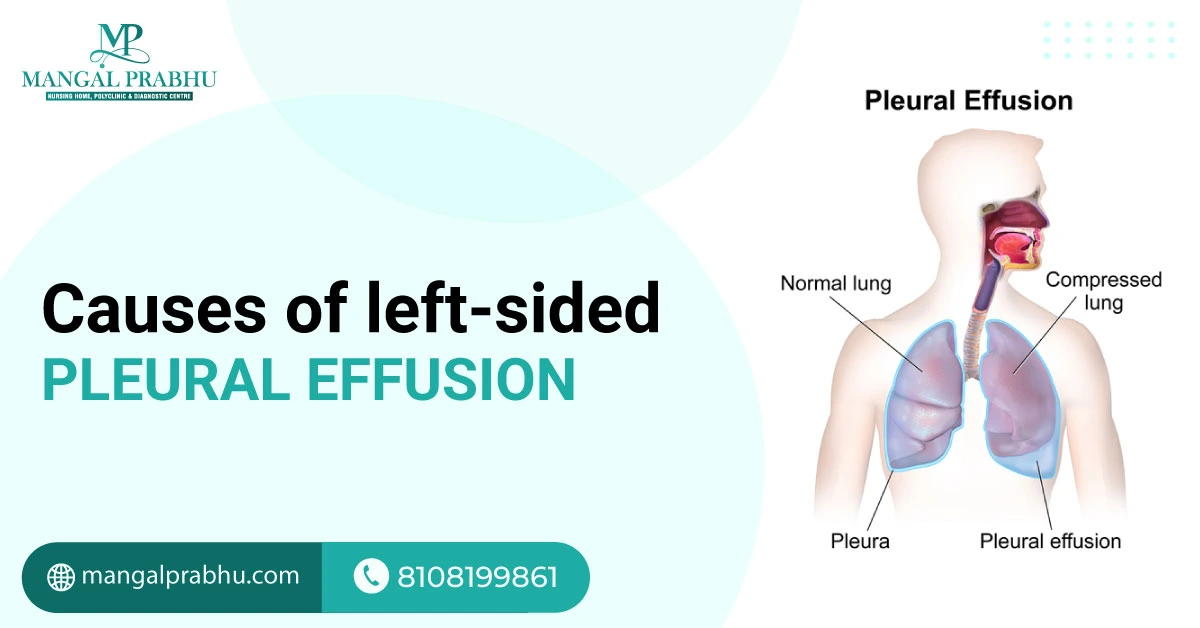
The pleura is described as a thin membrane lining the outside of your lungs and the chest walls. These naturally contain a small amount of fluid, which is produced to ensure smooth lung movements when you breathe. However, if a considerable volume of fluid is collected in the pleura cavity, it can indicate pleural effusion. A pulmonologist in Navi Mumbai will recommend medicine to fix it or a procedure that drains the excess fluid. Usually, the treatment focuses on identifying and treating the underlying cause.
Causes of Left-Sided Pleural Effusion
a) Heart-related Conditions:
Congestive heart failure is the common cause of left-sided pleural effusion. Your heart’s inability to pump blood sufficiently can lead to excess fluid accumulation in your pleural cavity. This is usually bilateral but can be one-sided. In some patients, pleural effusion occurs after cardiac surgery. Inflammation of the pleural cavity, an infection, or heart failure after surgery are the common causes.
b) Pulmonary conditions:
People with pneumonia and tuberculosis can develop pleural effusion. The infection can extend to the pleural cavity, filling it with fluid. Pulmonary embolism is another condition that increases the risk of pleural effusion. It happens when a blood clot gets into an artery in the lungs, causing a blockage. This blockage affects blood flow, resulting in fluid leakage into the pleural cavity.
Other Potential Causes
i) Trauma:
A serious heart injury that causes bleeding from the chest can lead to left-side pleural effusion.
ii) Autoimmune Diseases:
Your immune system can mistakenly attack your body’s tissues and organs. Lupus and rheumatoid arthritis are common examples of autoimmune diseases that can lead to pleural effusion.
iii) Cancer:
Lung cancer can cause fluid collection in the pleural cavity. Other cancers, like breast cancer or gastrointestinal cancer in their metastasis stage, can also spread to the pleural cavity, causing fluid buildup.
Diagnostic Approach
The healthcare provider will carefully examine your lungs at the pleural effusion treatment hospital in Navi Mumbai. They will ask about your symptoms and order imaging tests if needed.
A chest X-ray, for example, can show pleural effusion by highlighting the fluid in white while the rest of the space appears black. An ultrasound and CT scan might be needed to get a detailed picture of your chest and the pleural cavity. A minimally invasive procedure called thoracentesis is conducted to collect fluid samples from your pleural cavity using a catheter. This sample is sent to a lab for a thorough evaluation.
Treatment Options
Your doctor will address the underlying cause of the fluid buildup. If it’s caused by an infection, they will prescribe antibiotics to clear it. If it’s due to heart failure, diuretics might be used to reduce excess fluid from your body. Bronchodilators and NSAIDs can be used to help manage your symptoms. Thoracentesis is a medical procedure that involves inserting a needle into your pleural cavity to remove fluid and improve your breathing. Usually, treatment is decided based on the severity of the pleural effusion and its underlying cause.
Types of Respiratory Failure
Have you ever experienced feeling like you aren’t getting enough oxygen? Or do you have an abnormal breathing pattern (too fast or slow)? This can indicate respiratory issues. Respiratory failure is a medical condition that indicates too much carbon dioxide in your system or insufficient oxygen supply to the blood. This could happen suddenly or gradually.
To help you identify whether you need emergency medical treatment for respiratory failure in Navi Mumbai, we’ve curated this post that explains different types of respiratory failure, their symptoms, and treatment. Let’s take a look.
Type I
Respiratory Failure (Hypoxemic)
Hypoxemic respiratory failure occurs when the lungs cannot deliver sufficient oxygen to the bloodstream, which is supposed to pass to the tissues and organs. The lungs might be efficiently removing carbon dioxide but fail to deliver oxygen to the blood.
It could be because of pneumonia or fluid buildup in your lungs, which can block the oxygen flow. Pulmonary embolism (a condition where a blood clot travels to your lungs, affecting the oxygen flow) can also cause Hypoxemic respiratory failure.
Symptoms of Hypoxemic
- Shortness of breath
- Headaches
- Cyanosis (your skin turning blue from lack of oxygen)
- Wheezing
Treatment of Hypoxemic
This type of respiratory failure requires oxygen therapy, which is delivered through nasal prongs, masks, and ventilators.
Type II
Respiratory Failure (Hypercapnic)
Hypercapnia is another respiratory failure in which too much carbon dioxide builds up in the blood, making little to no room for oxygen to be transported to the tissues and organs. Carbon dioxide is a waste product that is expelled from the blood through the lungs. If the lungs aren’t functioning well, CO2 can accumulate in the blood, making it acidic.
Common causes include sleep apnea, chronic bronchitis, asthma, and neurological disorders. If you have hypercapnia, you are likely to experience these symptoms:
Symptoms of Hypercapnic
- Extreme fatigue
- Drowsiness and dizziness
- Tremors
- Anxiety
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
Treatment of Hypercapnic
A CPAP device keeps your airways open and ensures optimum airflow. This helps remove CO2 and aids in oxygen flow to your bloodstream. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause. Inhalers, for instance, are administered to patients with asthma.
A pulmonologist in Navi Mumbai will carefully examine your lung health and conduct blood tests, CT scans, or X-rays to assess the level of damage. If the damage is severe, a surgical intervention, such as a lung transplant, might be needed.
Acute vs. Chronic Respiratory Failure
If you develop acute respiratory failure, seek medical care. It occurs when your lungs stop functioning abruptly due to a trauma or a medical issue. Apart from trauma, sepsis and certain medication can affect your lung function. Symptoms include rapid breathing, shortness of breath, and panic attacks.
Chronic respiratory failure happens over time. Medical conditions, such as COPD or sleep apnea, can impair your lung function. Symptoms include fatigue, difficulty carrying out routine physical tasks, wheezing, and chronic cough.
Treatment for both requires oxygen therapy and medication to treat underlying medical issues.
Conclusion
Respiratory failure can be a life-threatening medical issue. It’s important to seek medical care, especially if you suspect acute respiratory failure. Your healthcare provider will help you understand your treatment options.

Difference between Bronchitis and Pneumonia
You have a runny nose and a bad cough, and you seem to have chest congestion. How do you know if it’s a common cold or a respiratory illness? Bronchitis and Pneumonia are the two most common terms we encounter regarding respiratory diseases. Both are respiratory issues and have pretty similar symptoms.
So, how do you differentiate between them? A pulmonologist in Navi Mumbai can help you determine whether it’s pneumonia, bronchitis, or a common cold. In the meantime, here’s all you should know about these respiratory conditions.
Understanding Bronchitis
Bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes, which carry oxygen to the lungs. These tubes can become infected, inflamed, and swollen. It can be acute or caused by viruses or bacteria.
Causes of Bronchitis
Viruses mainly cause bronchitis, but in some cases, bacteria can be the culprit. In either case, the germs enter your bronchial tubes, and as your body tries to fight off the infection, the tubes get inflamed and swollen, making breathing difficult. Chronic bronchitis occurs in people who smoke cigarettes, inhale polluted air regularly, and live in a dusty environment.
Symptoms of Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis lasts a few weeks. Common symptoms include:
- A feeling of heaviness and fullness in the chest
- Yellow, green, or clear mucus
- Excessive coughing
- Runny nose
- Wheezing noise during breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Fever and chills
- Sore throat
Treatment of Bronchitis
Bronchitis can go away on its own within a few weeks. If it’s caused by bacteria, your doctor may recommend antibiotics. Inhalers are recommended for people with asthma, allergies, and chronic bronchitis. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking or quitting work in a place that exposes you to irritants and harmful chemicals.
Understanding Pneumonia
Pneumonia affects the tiny air sacs called alveoli, which carry oxygen into the bloodstream. An infection can fill these air sacs with mucus, affecting their ability to contract and expand normally.
Causes of Pneumonia
Pneumonia can be bacterial, viral, or fungal. It happens when the germ enters the alveoli, which get swollen and filled with fluid as your immune system fights the infection. Pneumonia is more common in older people, babies, and people with weakened immunity.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia has similar symptoms to bronchitis. People with pneumonia experience:
- Cough that produces green or yellow mucus
- Chest tightness
- Chills and sweating
- Nausea
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Headache
- Blue lips
Treatment of Pneumonia
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the cause of the infection. If it’s bacterial, antibiotics are prescribed. If it’s viral, antiviral drugs can relieve your symptoms. Hospitalization might be needed in severe cases, although that’s not common.
Key Differences between Bronchitis and Pneumonia
Bronchitis occurs in the bronchial tubes, while pneumonia affects the air sacs. Bronchitis is mostly caused by viruses. Pneumonia, on the other hand, is bacterial but can be caused by viruses and fungi. Symptoms of pneumonia are more severe and can include confusion and blue lips, while bronchitis has flu-like symptoms, which aren’t that serious.
Conclusion
See your doctor immediately if you have a severe cough with mucus, shortness of breath, or chest pain. The sooner you get respiratory disorder treatment in Navi Mumbai, the faster you will recover.

Symptoms of Lung Disease in Females
Lung diseases affect individuals of all genders, and while there are common symptoms associated with these conditions, you must recognize that some symptoms may manifest differently in women. Understanding the symptoms of female lung diseases is essential for early detection, diagnosis, and timely treatment. In this blog, you can explore all information related to lung diseases in women.
Common Symptoms of Lung Disease in Females
Lung diseases can encompass a range of conditions, each with its unique symptoms. However, several common symptoms are often observed in females with lung diseases:
i) Shortness of Breath
One of the primary and often early symptoms of lung disease in females is shortness of breath.
ii) Coughing
A persistent, chronic cough is another prevalent symptom in women with lung disease.
iii) Chest Pain
Chest pain or discomfort can be associated with lung disease, particularly related to inflammation or infections.
iv) Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound produced during breathing and is common in lung diseases such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Also Read: Tips to Reduce Pulmonary Fibrosis Risk!
Causes of Lung Disease in Females
Several factors contribute to the development of lung diseases in females, with some of the primary causes being:
- Smoking is a major risk factor for lung disease. Women who smoke are at increased risk for conditions such as chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and lung cancer.
- Women exposed to high levels of air pollution, secondhand smoke, or occupational hazards are more vulnerable to lung diseases.
- Family history and genetics can also influence a woman’s susceptibility to lung diseases. Conditions like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency are genetically inherited and can lead to lung issues.
Diagnosis and Treatments
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing lung diseases effectively. Here are some diagnostic methods:
- Pulmonary Function Tests: These assess lung function and help diagnose conditions like asthma and COPD.
- Chest X-rays and CT Scans: Imaging tests provide detailed information about the condition of the lungs and help identify issues like tumors or infections.
- Blood Tests: Blood work may reveal signs of inflammation or infection.
- Bronchoscopy: This procedure involves a thin, flexible tube with a camera to view the airways and take samples if needed.
The Lung Disease Treatment in Navi Mumbai for Females includes:
A) Medication
Depending on the diagnosis, medications may be prescribed. These can include bronchodilators, corticosteroids, antibiotics, or antiviral drugs, among others. Lung specialists at Mangal Prabhu Hospital also use Inhalers and nebulizers for managing respiratory symptoms.
B) Surgery
In severe cases, surgical interventions such as lung transplantation or lung volume reduction surgery may be considered.
C) Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications are integral to managing lung diseases. It includes quitting smoking, avoiding environmental triggers, and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Conclusion
Lung diseases can affect females of all ages and backgrounds. Recognizing the common symptoms and seeking timely treatment is essential in managing these conditions. For residents of Navi Mumbai seeking lung disease treatment and consultation with a pulmonologist, Mangal Prabhu Hospital offers advanced facilities and experienced healthcare professionals.
If you or a loved one experiences any symptoms of lung disease, don’t hesitate to consult a Pulmonologist in Navi Mumbai for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Early intervention and proper management can make a significant difference in the quality of life for individuals dealing with lung diseases.
Tips to Reduce Pulmonary Fibrosis Risk!
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that thickens your lung tissues and causes scarring. The disease affects the lung, the surrounding tissues, and the air sacs, affecting the ability of the lungs to expand normally. As a result, the patient experiences difficulty breathing, dry cough, and fatigue.
You can see a general physician in Navi Mumbai to identify the symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis and figure out the most suitable treatment. However, the condition has currently no cure. We’ve listed some ways you can reduce the risk of developing the disease. Let’s take a look.
How To Reduce the Risk of Pulmonary Fibrosis
Unfortunately, there is no certain way or a proven method to prevent pulmonary fibrosis, but a few right steps can reduce your risk of developing the condition and managing it if you are already diagnosed with this lung disease. Here’s what may help.
1. Avoid Dust Exposure
One of the many risk factors for developing pulmonary fibrosis is exposure to dust and fumes. Working in a place where you are exposed to dust can put you at an increased risk of respiratory diseases, which can eventually result in pulmonary fibrosis. To lower your risk of the condition, it’s advisable to avoid exposure to dust and other harmful elements as much as possible.
2. Quit Smoking
Smoking causes inflammation in your lungs and creates thick mucus, which increases your risk of developing chronic lung diseases, lung cancer, and pulmonary fibrosis. Not just that, but smoking can make the disease worse. If you have pulmonary fibrosis, you must quit smoking right away to prevent the disease from worsening.
3. Get Treatment for Lung Infections
Chronic lung diseases develop gradually and worsen over time when left untreated. It’s important that you see a doctor if you notice any signs of infection. Infections like flu and pneumonia can weaken your lungs, making them vulnerable to chronic lung conditions. Getting vaccinated for such conditions is important to reduce the risk of pulmonary fibrosis and other lung diseases.
Also Read: COPD: Symptoms And Stages
Treatment for Pulmonary Fibrosis
While there is no permanent cure for pulmonary fibrosis, you must visit the pulmonology treatment center in Navi Mumbai to discuss the treatment options for managing the disease and slowing its progression.
- Oxygen Therapy: If the levels of oxygen are found in lower than normal volume, the healthcare expert might recommend you get oxygen therapy either through the oxygen tank or nasal cannula. However, it doesn’t cure pulmonary fibrosis. The therapy can improve your quality of life by managing your symptoms and helping you breathe comfortably.
- Medication: Based on your health, you might be advised to take certain medications to get relief from the symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis. Immunosuppressants and bronchodilators are commonly prescribed to patients at risk of developing lung conditions or those diagnosed with chronic lung disease.
- Lung Transplant: In some cases, a lung transplant might be needed to recover from the condition. If your lungs have been severely damaged, the doctor will advise you to replace them with healthy donor lungs.
Conclusion
The prevention of pulmonary fibrosis is essential for preserving respiratory health and overall well-being, to sum up. People can significantly reduce their risk of developing pulmonary fibrosis by adhering to the advice provided in this blog, such as quitting smoking, avoiding dust exposure, and seeking early medical intervention for any respiratory symptoms.
Always remember that prevention is always preferable to treatment and that protecting your lungs is an investment in your long-term health. Remain informed, look after your respiratory system, and put your health first. By doing this, you can live a healthier life and lower your risk of developing pulmonary fibrosis.

COPD: Symptoms and Stages
A lung condition called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) makes it difficult to breathe. As COPD is a progressive illness, it deteriorates over time and can ultimately result in disability or death.
Long-term exposure to irritants like tobacco smoke, air pollution, chemical fumes, or dust is usually what leads to COPD. The most typical signs of COPD include chest tightness, wheezing, chronic coughing, and shortness of breath.
These symptoms may appear gradually over time and be misdiagnosed as normal aging symptoms or the effects of a sedentary lifestyle. In a Multispecialty Hospital in Navi Mumbai, lung function tests, physical exams, medical histories, and imaging tests like X-rays and CT scans are all used to diagnose COPD.
Most typical signs and symptoms include:
- Breathing problems, especially when exercising
- chronic cough that frequently produces mucous
- loud or wheezing breathing
- stiffness or discomfort in the chest
- Weakness and weary
- respiratory diseases that are common
- Unwanted loss of weight
- Emboli in the legs, feet, or ankles
Also Read: 5 Factors To Consider While Choosing A Right Multispecialty Hospital
4 Stages of COPD:
Stage 1 (Mild):
In stage 1 COPD, the forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) is equal to or greater than 80% of the expected normal value. The airflow limitation is also minor. At this point, patients may have a persistent cough and more mucus than usual, but they might not feel noticeably short of breath.
Stage 2 (Moderate):
The FEV1 ranges from 50 to 80% of the expected normal value in stage 2 COPD, which is characterized by moderate airflow limitation. Those who are in this stage could feel coughing and mucous production, as well as shortness of breath when exercising.
Stage 3 (Severe):
The FEV1 is between 30 and 50 percent of the expected normal value in stage 3 COPD, which is characterized by significant airflow limitation. At this point, patients may also have other symptoms like weariness, recurrent respiratory infections, and even more severe shortness of breath.
Stage 4 (Very Severe):
The FEV1 is less than 30% of the expected normal value in stage 4 COPD, or less than 50% in respiratory failure. The airflow limitation is quite severe at this stage. People might have very little airflow at this point, along with major constraints on everyday activities, an oxygen dependency, and a lower quality of life.
According to a General Physician in Navi Mumbai, the severity of the condition and the patient’s particular symptoms determine whether a nebulizer should be used for COPD treatment. Nebulizers are generally utilized by those with moderate to severe COPD who have trouble using inhalers or other forms of treatment.
Emphysema
Emphysema is a kind of COPD, and the severity of the condition is normally determined by the outcomes of lung function tests. The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) approach, which classifies COPD into four stages based on the severity of airflow limitation, is the most widely used COPD staging system.
The severity of the condition and the patient’s particular symptoms determine whether oxygen therapy is required for COPD. Those with severe COPD, which is often categorized as Stage 3 (Severe) or Stage 4 (Very Severe COPD), are generally advised to use oxygen therapy. Using supplementary oxygen to improve blood oxygen levels and assist in treating symptoms including exhaustion, disorientation, and shortness of breath is known as oxygen therapy.
